VOC-Free Waterborne Polyurethane Epoxide Resin and Crosslinker for Producing Tough and Flexible Coatings (RFT-154/154A)
Invention Summary
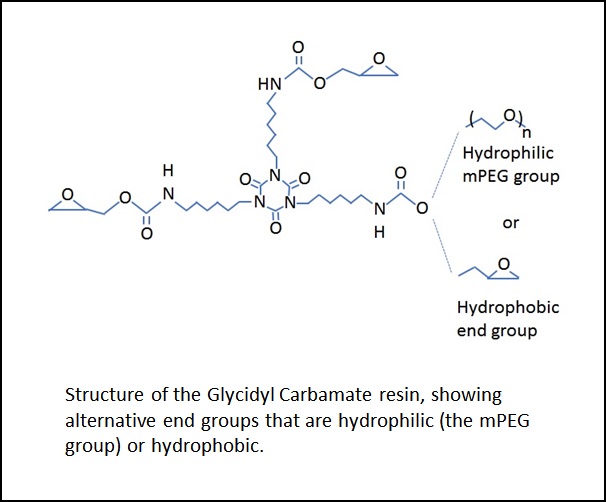
Scientists at North Dakota State University have developed a polyfunctional waterborne Glycidyl Carbamate (GC) resin, comprising oligomers that provide polyurethane properties with epoxide reactivity. These compounds can be dispersed in water to form a dispersion containing no volatile organic solvent. The tough and flexible coatings produced using this material have high hardness and durability as well as high gloss. A particularly promising application is to use GC crosslinkers as a very minor ingredient in lubricious and other "fragile" coatings, where it provides substantially increased strength with minimal impact on other properties. A commercial advantage of this resin is not having isocyanate water reactions, or isocyanate toxicity concerns, but having controlled and safer reactions with amines or other reactive functionality. The technology is a waterborne, solvent-free glycidyl carbamate resin. These resins are produced by reaction of an isocyanate functional resin with glycidol, resulting in a GC product that includes urethane and epoxy functional groups. Aliphatic polyisocyanate is made water dispersible by additions of mPEG, and end capped with glycidol to produce glycidyl functionality that crosslinks. These may then be crosslinked by reaction with amines, or may self-crosslink at elevated temperature.
Benefits
- May be used as a resin or crosslinker
- Very small amounts dramatically increase hardness and durability without negatively impacting lubricity
- Excellent water resistance, solvent resistance, and flexibility
- Ambient cure temperature
- No VOCs
- Transparent, with no phase change or haziness
- High gloss
Patents
This technology is the subject of US Issued Patent Nos. 7,776,956 and 9,676,895 and is available for licensing/partnering opportunities.
Contact
NDSU Research Foundation
info(at)ndsurf(dot)org
(701)231-8173
NDSURF Tech Key
RFT, 154, RFT154
Inquire about this technology >