Contactless Laser-Assisted Placement of Discrete Electronic Components (RFT-370)
Invention Summary
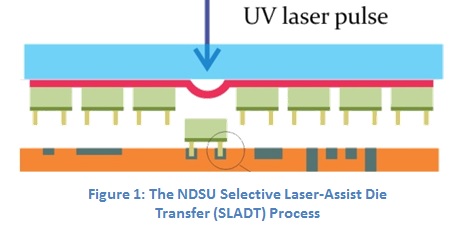
Scientists working at North Dakota State University (NDSU) have discovered a method for the contactless laser-assisted assembly of discrete components such as ultra-thin, ultra-small semiconductor dies and MEMS components onto rigid and flexible substrates. Laser-direct write techniques are an enabling technology for the ever-decreasing scale of microelectronic devices. Specifically, Laser Induced Forward Transfer (LIFT) techniques show promise as a disruptive technology which will enable the placement of components smaller than what conventional pick-and-place techniques are capable of today. NDSU’s Thermo-Mechanical Selective Laser Assisted Die Transfer (tmSLADT) process is an application of the unique blistering behavior of polyimide film when irradiated by low energy focused ultraviolet laser pulses. The tmSLADT process has the potential to take its place as the next generation LIFT technique, with distinct advantages over previously studied ablative and thermal releasing techniques. Experimental results studying transfer precision indicate this non-optimized die transfer process compares with, and may exceed, the placement precision of current assembly techniques.
Benefits
- Contactless process
- High-volume assembly of small size, ultra-thin semiconductor bare dies
- The tmSLADT process can package dies with sizes well below the lower limit of conventional manufacturing technologies
- Packaging is about 10 times faster compared to that found in conventional methods
- The significantly smaller die size reduces the cost of assembly and silicon by an order of magnitude
Applications
- RFID tags
- Smart cards
- Micro-sensor systems
- Wearable electronics
- LEDs
- Micro-sized solar cell modules
Patents
This technology is the subject of US patent No. 9,862,141.
Status
Licensed Exclusively in all Fields of Use and in all Territories
Contact
NDSU Research Foundation
info(at)ndsurf(dot)org
(701)231-8173
NDSURF Tech Key
RFT, 370, RFT370
Inquire about this technology >