Vegetable Oil-Based Polymers for Nanoparticle Surface Modification (RFT-413)
Invention Summary
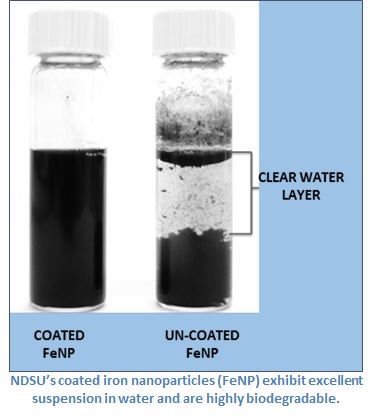
The extremely high surface area of nanoparticles provides many advantages over conventional particles with dimensions in the micron scale. For a variety of applications, it is necessary to suspend the nanoparticles in a liquid medium. Researchers at NDSU have developed a new plant-oil-based polymer technology focused on the application of nanoparticle suspension in water. One primary example of this technology application is its use as a protectant while dispersing and suspending iron nanoparticles in decontamination efforts involving chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as tetrachloroethylene. The copolymers described herein are not only highly effective with respect to suspending nanoparticles in water, but also exhibit high biodegradability. Biodegradability is important for environmental applications because the polymer is typically not recovered after treatment of a groundwater contaminant plume. In addition, compared to other approaches, this copolymer technology enables compositions to be highly tailored or optimized for a given nanoparticle and application.
Benefits
- Biodegradable
- Increased Dispersion and Suspension in Water
- Multiple Applications
- Novel Protected Composition
Applications
- Ground Water Remediation
- Detergents
- Production of Carbon Coatings
- Conductive Inks
Patent
This technology is the subject of Issued US Patents 9,487,420 and 9,631,040 and is available for licensing/partnering opportunities.
Contact
NDSU Research Foundation
info(at)ndsurf(dot)org
(701)231-8173
NDSURF Tech Key
RFT, 413, RFT413
Inquire about this technology >