SOY PROTEIN DERIVED HYDROGEL FOR SENSING APPLICATIONS (RFT-677)
Invention Summary
This technology introduces the first soy protein-based
double network (DN) ionic conductive hydrogel, engineered for enhanced
mechanical and conductive properties. The hydrogel consists of a methacrylated
soy protein isolate (MSPI) and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) double network,
combined with tannic acid-coated cellulose nanocrystals (TCNC) and sodium
chloride (NaCl) in a glycerol-water binary solvent system
Benefits
- Enhanced durability: Robust against mechanical stress, freezing, and drying, ensuring longevity in various environments.
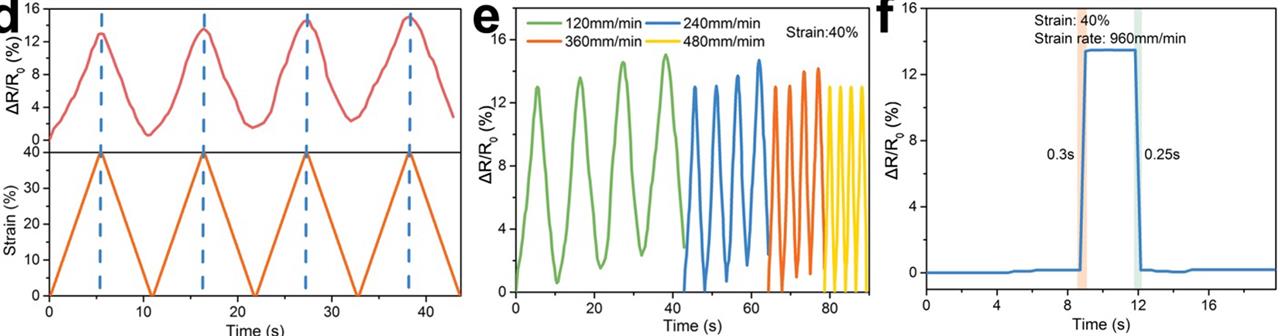
- High Performance: Exceptional strain sensitivity and response time (~300 ms), capable of detecting diverse human movements with high accuracy
- Biocompatibility: Made from soy protein, a natural and abundant material, making it environmentally friendly and suitable for biomedical application
Applications
- Wearable Electronics: Ideal for flexible sensors in health monitoring devices and human-machine interfaces
- Medical Devices: Applicable in implantable devices and drug delivery systems due to its biocompatibility
- Soft Robotics: Suitable for constructing flexible and durable components in soft robotic systems
- Personal Hygiene Products: Can be used in advanced personal care items requiring high flexibility and durability
Patent
This technology has a U.S. Patent Pending
and is available for licensing/partnering opportunities.
Contact
NDSU Research Foundation
info(at)ndsurf(dot)org
(701) 231-8173
NDSURF Tech Key
RFT, 677, RFT677
Inquire about this technology >